
You’ve probably seen a million and one product manager vacancies on the internet and are still wondering “what does a product manager do?” There is nothing wrong with that, trust me. Moreso, this is why I am here to help out as always.
The lack of familiarity with the function of product manager is most likely due to its newness. Whereas more established professions like design and engineering have been able to segment themselves by speciality, product managers are still trying to figure out what their job should be.
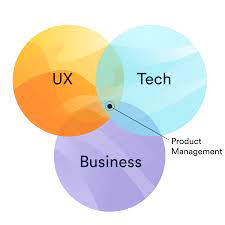
In a nutshell, a product manager is a person who works at the convergence of business, technology, and user experience.
Sounds even more complicated, yeah? It isn’t Let’s break it down.
Who is a Product Manager?
 You are eager to find an answer to your question yet, you’re unaware of who a product manager is?
You are eager to find an answer to your question yet, you’re unaware of who a product manager is?
A product manager finds the consumer demand and bigger company objectives that a product or feature will meet, articulates what success looks like for a product, and rallies a team to make that vision a reality.
Roles and Responsibilities
A product manager is in charge of a product’s strategy, roadmap, and feature definition. Product marketing, forecasting, and profit and loss (P&L) tasks may also be part of a product manager’s job description. Product managers examine market and competitive situations before sketching out a differentiated product vision that delivers unique value based on client needs.
Visionaries make the finest product managers. You are in charge of a product’s success and the cross-functional team that is in charge of improving it. This is a critical organizational job, particularly in technology firms. Product managers are responsible for leading and making strategic product choices.
While product managers have been referred to as “mini-CEOs,” it is more true to describe you as the product leaders at the crossroads of business, technology, and user experience (UX). This is due to the fact that the role encompasses a wide range of operations, from strategic to tactical, and provides critical cross-functional leadership, particularly amongst engineering, marketing, sales, and support teams. The responsibilities of a product manager includes:
Related: Duties of a product manager
Establishes the product’s vision and road plan
This entails creating a product roadmap and an overall production plan to achieve the company’s vision and goals, based on the company’s vision and the desired output of a product.
Collecting and evaluating user feedback, as well as working with cross-functional teams to define the product’s future trajectory, are all necessary steps in establishing the product vision. This will entail looking over the product backlog and identifying and prioritizing which new features will be implemented.
Analyzes the requirements of customers
Searching for, gathering, handling, and prioritizing client needs and wants is one of a product manager’s responsibilities. Knowing what the market wants is essential for a successful product. They must comprehend both why customers purchase things and what the competition is doing.
Product managers must participate in customer experience interviews to collect consumer input and understand customer needs by both taking what they say at face value and inferring needs from their feedback in order to design a user experience that will please customers. A product manager will collaborate closely with the customer service team to identify major pain points that the present product does not cover, as well as how to develop solutions to meet this input.
Be a proponent
A product manager’s job description includes the obligation of advocating for customers and their demands. If there are concerns about whether the product is adequately targeting the market, the product manager must argue for the customer’s needs.
It’s all too easy for the engineering team to believe that what they produce as a solution would be understood by the customers without any additional instruction. A successful product manager will be able to use customer input to assess whether the consumer is receiving the greatest possible user experience.
A product manager will keep the company’s goals in mind at all times and play an important role in the decision-making process to guarantee that the product satisfies the needs of the consumer.
Assemble the team
In the product management process, there are many actors, and the product manager must ensure that engineering, sales, marketing, and customer service are all working together to satisfy the business case and customer objectives.
A product manager must understand how to ensure effective team cross-functionality. This necessitates clear communication protocols to ensure that everyone understands the overarching product vision.
Evaluating programs
Product managers are in charge of performing beta and pilot programs as the product nears completion. They also assess finished work on a regular basis to ensure that the product meets client requirements. In addition, they monitor product modifications as needed.
In order to receive timely feedback and make improvements, a product manager needs to be familiar with the agile framework. A product manager will want to know what worked well in the pilot programs. They also seek how to enhance the product in future iterations by evaluating consumer feedback.
Be an innovator
Product management is responsible for developing new business cases for new goods. Also, improving existing ones and seeking out new commercial possibilities.
As previously said, a product manager should consider themself to be the product’s CEO. A product manager can decide whether consumer wants can be addressed. He iterates on the current product or whether a new product would be a superior concept by doing ongoing user research.
Work as a presenter
The task of providing complete reporting and documentation is an important component of a product manager’s job. Business cases, market needs documents, and product roadmaps are just a few examples.
Others, such as case studies, product comparisons, and competitive analysis, might be required. Product management will also include a significant amount of documentation for presentations and data sharing.
A product manager must be a storyteller. Must use facts and metrics to back up claims in order to effectively communicate client needs.
A P.M must be able to bridge gaps. Especially between product development teams and the product’s final journey to market. A competent P.M will be able to foster strong collaboration among cross-functional teams. Such teams include the product team, engineering team, sales team, and customer service team.

